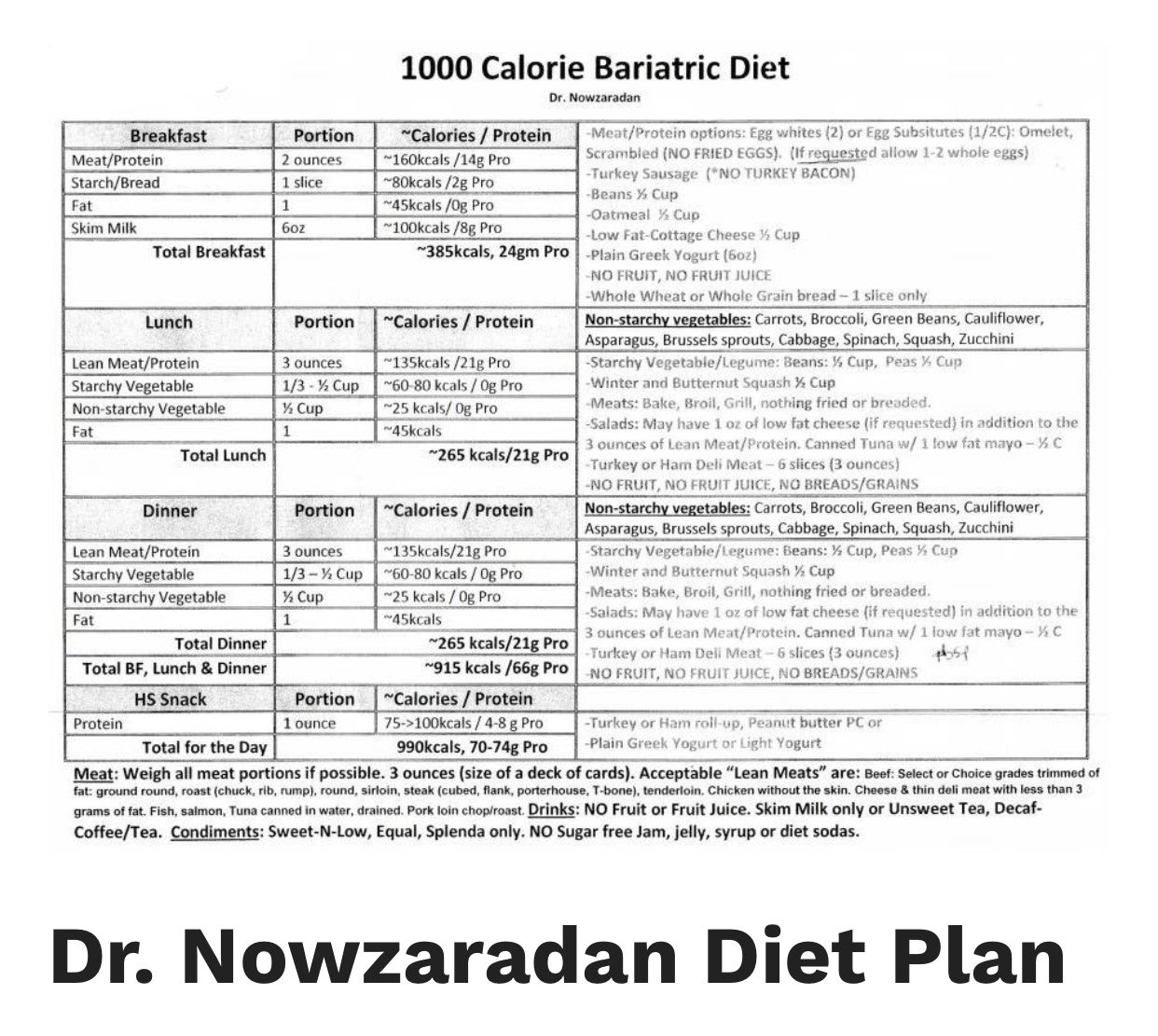
Comprehensive Guide to Arctic Fox Diet: Essential Insights for 2025
The Arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) possesses a unique and adaptive diet that plays a crucial role in its survival in the harsh tundra ecosystem. Understanding what arctic foxes eat is essential not only for wildlife enthusiasts but also for conservation efforts aimed at protecting this fascinating species. Given the rapid changes in climate and habitat that are occurring, researchers are increasingly focused on the feeding habits of arctic foxes and how these may be influenced by fluctuating prey availability and environmental conditions.
This guide delves into the diverse food sources of the arctic fox, examining its foraging behavior and dietary needs throughout different seasons. We will explore various aspects of the arctic fox's ecology, including its hunting strategies, prey preferences, and how competition and climate change shape its dietary patterns. By the end of this article, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the arctic fox diet and its significant role within the tundra ecosystem.
Key takeaways include insights into the arctic fox's ecological role, the implications of a changing climate on its feeding habits, and strategies for the conservation of this remarkable species.

Essential Components of the Arctic Fox’s Diet
At the heart of understanding the arctic fox's dietary habits is recognizing the variety of food sources available in its environment. The arctic tundra diet comprises mainly small mammals, birds, and carrion, each playing a vital role across the different seasons.
Small Mammals in the Arctic Fox Diet
One of the primary food sources for arctic foxes is small mammals, particularly lemmings and voles. These rodents fluctuate in population size, which influences the arctic fox's hunting success. During peak lemming years, the arctic fox nutrition significantly improves due to the abundance of this high-energy prey. Conversely, in years of low lemming availability, foxes must adapt their hunting strategies or risk starvation.
Additionally, the consumption of small mammals also supports the ecological balance of tundra environments, illustrating the interconnectedness of predator and prey. As such, understanding the dynamics of lemming populations is vital for assessing the overall health of arctic ecosystems.
Bird Species in the Arctic Fox Diet
Another significant component of the arctic fox's diet consists of ground-nesting birds and their eggs. Species such as ptarmigans and shorebirds contribute to the arctic fox food sources, particularly during summer months when their populations increase. The strategic ability of arctic foxes to hunt birds demonstrates their adaptability and opportunistic feeding behavior.
Moreover, observing how arctic foxes interact with bird species can highlight important behavioral patterns, such as seasonal migration of prey and nest predation rates.
Importance of Carrion and Scavenging
Arctic foxes are also adept scavengers, often consuming carrion from larger predators such as polar bears and seals. This scavenging behavior is critical for their survival during harsh winters when active hunting proves more challenging. By utilizing available carcasses, they ensure a diversified diet, which further emphasizes the importance of arctic fox scavenging behavior.
Understanding this feeding habit sheds light on the arctic fox's ecological role, highlighting its function as both a predator and scavenger within the tundra food web.
Seasonal Diet of the Arctic Fox
The diet of the arctic fox changes significantly with the seasons, responding to the availability of different food sources. This adaptability showcases the species' remarkable survival strategies in a challenging environment.
Winter Diet Considerations
During winter, the arctic fox often relies on its cache of food from the previous summer and fall. The arctic fox winter diet primarily consists of dispersed small mammals below the snow, such as rodents. Their acute hearing allows them to detect movements beneath the snow, making them proficient hunters even in challenging conditions.
This reliance on a stored food supply highlights the arctic fox's remarkable ability to instinctively assess and manage its food resources, a vital skill in the relentless tundra.
Spring and Summer Feeding Habits
As snow melts and vegetation begins to bloom in spring, arctic foxes expand their dietary intake to include a wider range of small mammals and bird species. The prevalence of lemmings during this time significantly boosts their nutritional intake, showcasing their adaptability and ability to thrive with seasonal changes in prey. The successful reproduction of small mammals boosts the arctic fox's reproductive success, as the abundance of food ultimately supports the survival of pups.
Autumn Diet Adjustments
In autumn, the feeding patterns of arctic foxes shift again as they prepare for winter. They engage in increased scavenging behavior, taking advantage of the abundance of carrion from deceased animals. This not only helps them build fat reserves for the colder months but also demonstrates their flexible dietary needs across the seasons.
Hunting Strategies and Foraging Behavior
To comprehend the intricacies of the arctic fox diet, we must delve into their hunting strategies and foraging behavior. Understanding these tactics reveals the intelligence and adaptability of arctic foxes, helping to connect them to their ecological niche.
Hunting Techniques of Arctic Foxes
Arctic foxes employ various hunting techniques that best suit their environment, such as pouncing on prey hidden beneath the snow. This unique method is not only efficient but also reduces energy expenditure, essential in their cold habitat. They may also use stalking techniques when hunting birds or small mammals in open landscapes.
Impact of Environment on Hunting Success
The arctic fox's feeding patterns are heavily influenced by environmental factors, including snow cover and temperature. Deep snow may hinder their ability to hunt effectively, prompting them to rely more on scavenging. Conversely, a favorable hunting environment may lead to an increase in hunting success, demonstrating the impact of habitat conditions on their food availability.
Social Behavior and Group Hunting
In some instances, arctic foxes may engage in social hunting behaviors, working together to catch prey or protect caches. Understanding these behaviors provides insight into the arctic fox social structure and its implications for survival in a competitive ecosystem. Cooperation in hunting can increase success rates, particularly in challenging conditions.
Climate Change and Its Impact on the Arctic Fox Diet
As climate change continues to reshape the Arctic landscape, it poses significant challenges for arctic foxes and their dietary habits. The changing climate affects prey availability and hunting success, prompting a reassessment of the species' adaptability.
Shifts in Prey Availability
Warm temperatures can lead to alterations in prey population dynamics, resulting in fluctuating food sources for arctic foxes. For example, the decline of lemming populations can significantly affect their diet, as small mammals become less available.
Effects of Habitat Loss on Diet
Habitat loss due to human impact and climate change disrupts the ecological balance of the tundra, threatening the arctic fox's ecological role and survival. As habitat fragmentation increases, food competition among species may heighten, leading to greater challenges for the Arctic fox in locating adequate food sources.
Adaptations to a Changing Food Web
Understanding the effects of climate change on the arctic fox diet is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. Monitoring patterns of dietary selection and prey availability helps researchers assess the impact of environmental shifts on the overall health of arctic fox populations.
Conclusion: The Importance of a Diverse Diet for Arctic Foxes
The arctic fox's diet is a key component of its survival, illustrating the intricacies of feeding strategies, prey interactions, and the consequences of environmental changes. Maintaining a diverse diet that includes small mammals, birds, and carrion is essential for the health and reproductive success of arctic foxes.
As we look toward the future, it's vital to continue studying the impacts of climate change and human influence on the arctic fox's feeding habits. Through targeted conservation efforts and further research, we can promote the preservation of this iconic species and its role within the fragile Arctic ecosystem.
Q&A Section: Understanding Arctic Fox Diet
What do arctic foxes primarily eat?
Arctic foxes primarily consume small mammals like lemmings and voles, birds, eggs, and carrion. Their diet can change based on seasonal availability and environmental conditions.
How do arctic foxes hunt?
Arctic foxes use various hunting techniques, including pouncing on prey beneath the snow and stalking small mammals or birds. Their hunting strategies are adapted to their icy habitat.
What impact does climate change have on arctic fox diets?
Climate change disrupts prey populations and affects hunting success. Changes in the environment may lead to dietary shifts due to the availability of food sources.
Do arctic foxes scavenge for food?
Yes, arctic foxes are opportunistic scavengers, often feeding on carrion from larger predators. This behavior is crucial for their survival, especially in winter months.
How does diet affect the reproductive success of arctic foxes?
A diverse diet—particularly during seasons with young pups—is critical for reproductive success. Abundant food sources support the growth of healthy offspring.